西宁市网站建设_网站建设公司_云服务器_seo优化
难度参考
难度:中等
分类:哈希表
难度与分类由我所参与的培训课程提供,但需要注意的是,难度与分类仅供参考。且所在课程未提供测试平台,故实现代码主要为自行测试的那种,以下内容均为个人笔记,旨在督促自己认真学习。
题目
给你两个字符串:ransomNote 和 magazine,判断ransomNote 能不能由magazine 里面的字符构成。如果可以,返回true;否则返回false
示例1:
输入:ransomNote ="a", magazine = "b"输出:false
示例2:
输入: ransomNote = "aa", magazine ="ab"输出:false
额外提示:
1 <= ransomNote.length, magazine.length <= 10(5)
ransomNote和magazine由小写英文字母组成
magazine中的每个字符只能在ransomNote中使用一次
思路
为了确认能否从 magazine 字符串中得到 ransomNote 字符串所需的所有字符,我们必须比较这两个字符串中各字符的出现次数。这可以通过以下步骤实现:
-
统计
magazine中字符的频率:
创建一个大小为 26 的数组或向量用以表示每个字母的计数器,因为假设字符串仅包含小写字母。遍历magazine并增加每个字符相对应的计数器。 -
检查
ransomNote的字符:
遍历ransomNote,对于每个字符,减少其在计数器数组中对应的值。如果在减少之前某个字符的计数器值已经是 0,说明magazine中没有足够的字符以形成ransomNote。 -
结果判断:
如果所有字符在减少计数器时都没有产生负值,即magazine含有足够的每个字符以构建ransomNote,则返回 true。否则,如果任何字符的计数器值变为负,说明magazine中缺乏足够的该字符,无法构建ransomNote,返回 false。
示例
假设我们有以下两个字符串:
ransomNote: “aab”
magazine: “baa”
我们想要检查是否可以从杂志字符串 “magazine” 中剪下字母构造出勒索信 “ransomNote”。我们的方法是按照字母计数来检查。以下是对应的步骤和发生的事情:
-
初始化字符计数:
我们创建了一个大小为 26 的数组或向量
charCount来记录每个字母的出现次数。因为我们只处理小写字母,所以我们不需要更大的大小。每个位置初始化为 0。 -
统计
magazine中的字符:对于字符串 “baa”,我们执行以下操作:
- ‘b’ ->
charCount['b' - 'a'](即charCount[1])将从 0 变成 1。 - ‘a’ ->
charCount['a' - 'a'](即charCount[0])将从 0 变成 1。 - 另一个 ‘a’ ->
charCount[0]将从 1 变成 2。
charCount向量现在包含:[2, 1, 0, 0, …, 0],因为 ‘a’ 出现了两次,‘b’ 出现了一次,其他字母出现了零次。 - ‘b’ ->
-
检查
ransomNote中的字符:对于字符串 “aab”,我们执行以下操作:
- ‘a’ ->
charCount[0]从 2 减到 1。 - 另一个 ‘a’ ->
charCount[0]从 1 减到 0。 - ‘b’ ->
charCount[1]从 1 减到 0。
在这个过程中,
charCount向量的每个相关位置至少为 0,这意味着magazine中每个所需字符的数量都足够ransomNote使用。 - ‘a’ ->
-
返回结果:
由于
charCount中没有任何索引变为负数,我们可以得出结论,在magazine中总是有足够的每个字符来构建ransomNote,因此函数返回 true。
这就是代码的基本工作原理。通过遍历 ‘magazine’ 增加计数,然后遍历 ‘ransomNote’ 减少计数,最后根据计数结果决定是否可以构建出 ‘ransomNote’。
梳理
这种方法之所以能够实现,是因为我们在检查能否从 `magazine` 得到 `ransomNote` 所需的所有字符时,遵循了两个基本原则:
1. 频率匹配原则:
每个字符在 `ransomNote` 中出现的频率不能高于在 `magazine` 中出现的频率。如果 `ransomNote` 需要比 `magazine` 提供更多的某个字符,这显然是不可能的,因为你不能从 `magazine` 中得到比它本身更多的某个字符。
2. 字符独立原则:
字符的使用是独立的。即,一个 'a' 的出现与另一个 'a' 的出现无关,它们可以独立计算。这使得我们可以通过简单地计数每个字符来跟踪 `magazine` 中有多少个 'a',而不必关心它们在字符串中的位置或顺序。
当我们使用一个大小为 26 的数组(针对 26 个小写字母)来统计 `magazine` 中各字母的出现次数时,我们就执行了一个由字符到频率的映射。由于 `ransomNote` 可能包含重复的字母,通过逐个检查并递减 `magazine` 中的相应字母计数,我们实际上是在确认是否对于 `ransomNote` 中的每个字符,`magazine` 都至少有相等数量的该字符。
这个检查过程中,如果发现某个字符在 `magazine` 中的计数已经为零(即已经被 'ransomNote' 用尽),然后 `ransomNote` 还需要该字符,那么说明 `magazine` 不能满足 `ransomNote` 的需求。
因为这种方法直接通过频率匹配来确定是否可行,所以它是高效且有效的。它不必关心两个字符串的任何其他复杂关系,如它们的子序列关系或排序。当我们完成了遍历整个 `ransomNote` 名称,并且没有发现任何计数不足以匹配需求的情况时,我们就可以确定 `magazine` 可以提供足够的字符来构建 `ransomNote`。
这类问题被称作"哈希表"问题,是因为它涉及到对数据的快速查找和访问,哈希表是实现这种操作的理想数据结构。在你给出的 C++ 代码示例中,charCount 数组充当了一个简化的哈希表的角色,用于快速统计和检索字母的出现次数。
哈希表(Hash Table)这一数据结构。哈希表是一种根据键(Key)直接访问在内存存储位置的数据结构。它使用一个哈希函数来计算一个值(键的哈希值),然后这个值决定了键在表中的位置。
详细来说,charCount 通过将字符 ‘a’ 到 ‘z’ 映射到数组的索引 0 到 25 来简化哈希函数。在这种情况下,索引表示字母的哈希值,而数组的值表示特定字母在杂志字符串 magazine 中出现的次数。这是由以下代码段实现的:
for (char ch : magazine) {++charCount[ch - 'a']; // 对于每个字母,计数器位置是 ch - 'a'
}
在上述代码段中,字符 ‘a’ 减去它自身 (‘a’ - ‘a’) 给出哈希值 0,字符 ‘b’ 减去 ‘a’ (‘b’ - ‘a’) 给出哈希值 1,依此类推,字符 ‘z’ 减去 ‘a’ (‘z’ - ‘a’) 给出哈希值 25。
这样,我们就创建了一个特定于问题的、基于字符的哈希表,不需要使用复杂的哈希函数或处理哈希冲突,因为英文字母的数量是限定的(26个字母),所以我们可以保证每个字母都有一个唯一的哈希值,并且可以直接映射到数组的索引。
之后在检查 ransomNote 字符串时,也使用到了这个哈希表来确认杂志字符串中是否包含足够数量的每个字母以构建 ransomNote。
这种对数据的快速访问和管理能力是哈希表的关键特点,也就是为什么这种类型的问题可以被归类为哈希表问题。在实际的应用中,哈希表通常是通过如 std::unordered_map 或 std::map 实现的,但基本概念与我们的简化模型相同。
代码
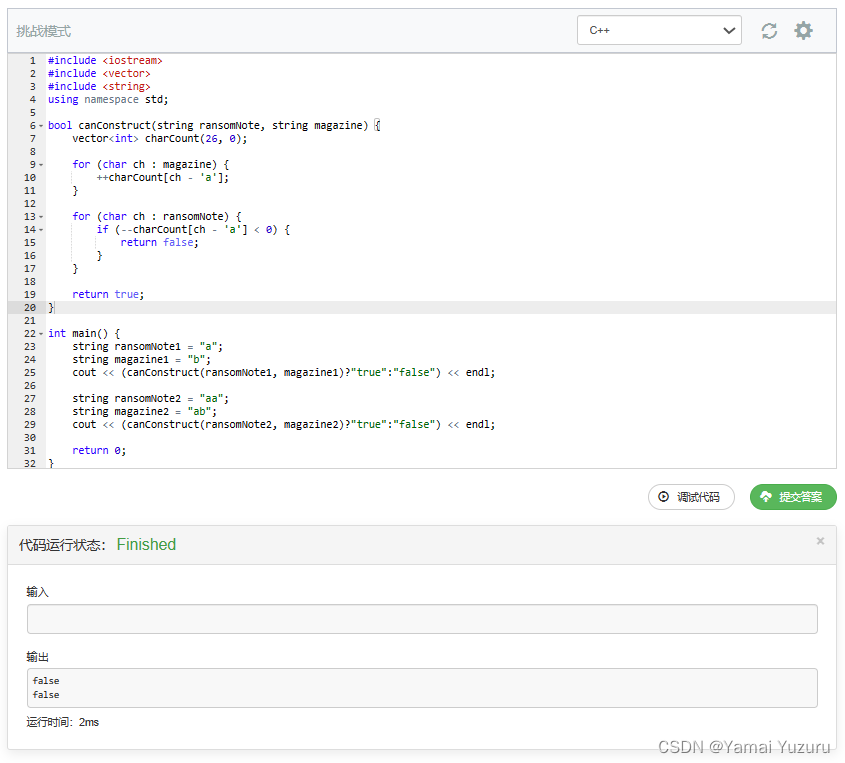
#include <iostream> // 包含输入/输出流库
#include <vector> // 包含 vector 容器库
#include <string> // 包含 string 类库
using namespace std; // 使用 std 命名空间,避免 std:: 前缀// 函数 canConstruct 用于判断是否能够通过 magazine 的字母构造出 ransomNote
bool canConstruct(string ransomNote, string magazine) {vector<int> charCount(26, 0); // 创建一个大小为 26 的整数向量,用于计数每个字符的出现次数,初始化为 0for (char ch : magazine) { // 遍历 magazine 中的每个字符++charCount[ch - 'a']; // 增加 magazine 中当前字符的计数}for (char ch : ransomNote) { // 遍历 ransomNote 中的每个字符if (--charCount[ch - 'a'] < 0) { // 减少 ransomNote 中当前字符的计数,如果计数小于 0 则返回 falsereturn false;}}return true; // 如果 ransomNote 中的所有字符都能在 magazine 中找到,则返回 true
}int main() {string ransomNote1 = "a"; // 初始化测试用例 1 的 ransomNote string magazine1 = "b"; // 初始化测试用例 1 的 magazine// 输出测试结果:使用可以构造的函数结果,并转换为 "true" 或 "false" 字符串cout << (canConstruct(ransomNote1, magazine1) ? "true" : "false") << endl;string ransomNote2 = "aa"; // 初始化测试用例 2 的 ransomNotestring magazine2 = "ab"; // 初始化测试用例 2 的 magazine// 输出测试结果:使用可以构造的函数结果,并转换为 "true" 或 "false" 字符串cout << (canConstruct(ransomNote2, magazine2) ? "true" : "false") << endl;return 0; // main 函数正常终止
}事实上还可以在开始前判断一下长度,长度不同直接否决,这边没写。
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(1)
打卡